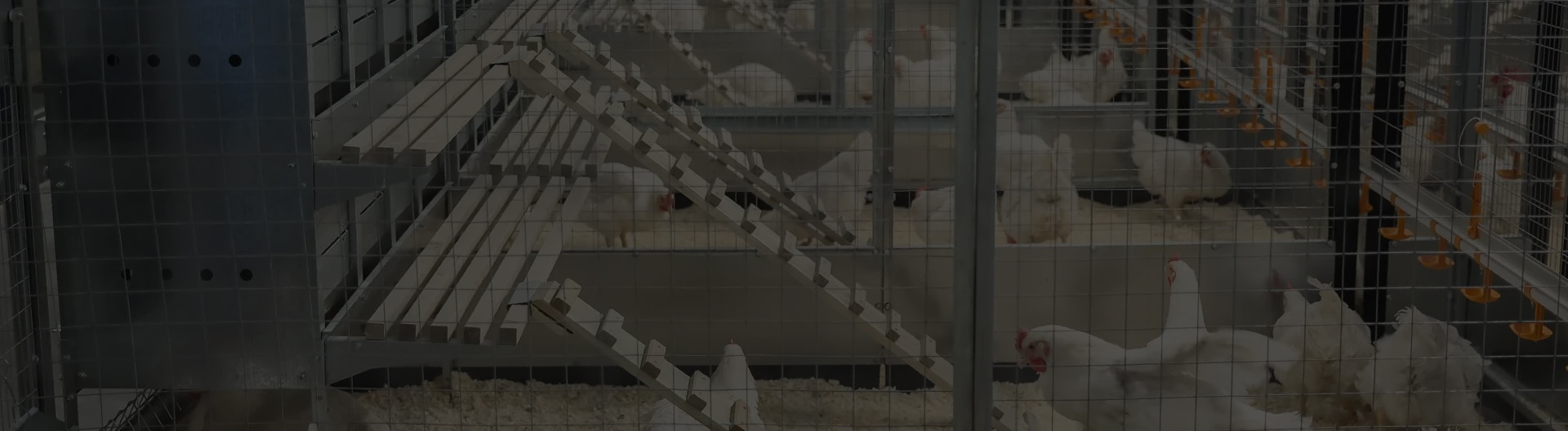
layer house in poultry
Aug . 31, 2024 01:33 Back to list
layer house in poultry
Layer House in Poultry Farming
The layer house is a crucial component in poultry farming, specifically in the production of eggs. Designed for housing hens that are raised for their egg-laying potential, a well-constructed layer house fosters a conducive environment for birds to thrive, ultimately ensuring optimal egg production. This article delves into the essential features, management practices, and advancements associated with layer houses.
Design and Structure
A layer house is primarily characterized by its design, which prioritizes the welfare of the hens while maximizing productivity. Modern layer houses are typically equipped with features such as proper ventilation, temperature control, adequate lighting, and space for movement. The space allocated for each hen is vital; overcrowded conditions can lead to stress, which adversely affects egg production and the overall health of the flock.
Good ventilation is crucial in layer houses. It helps in regulating temperature and removing harmful gases, thus providing a comfortable environment for the hens. Natural ventilation can be enhanced by strategically placing windows and vents, while mechanical systems can also be employed for more precise control. Lighting plays a significant role in layer production, as hens require specific light exposure to stimulate egg-laying. A combination of natural sunlight and artificial lighting is often used to create an optimal light cycle.
Management Practices
Effective management practices are essential to the success of a layer house. Biosecurity is the first step in fortifying the flock against diseases. This includes restricting access to the poultry house, implementing strict sanitation protocols, and maintaining a healthy flock through vaccinations and regular health checks. Ensuring that the hens are fed a balanced diet is also critical. The feed should be rich in nutrients and formulated to meet the specific needs of laying hens, focusing on protein, calcium, and essential vitamins to ensure optimal egg production.
layer house in poultry
Monitoring the health and productivity of the hens is vital for maintaining performance. Record-keeping practices enable farmers to track egg production rates, feed consumption, and overall bird health, thereby identifying trends that may necessitate intervention. Regular assessments allow for prompt action should any issues arise, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the layer house.
Technological Advancements
In recent years, technology has revolutionized layer house management. Automation systems for feeding, watering, and egg collection have significantly reduced labor costs and increased efficiency. Climate control systems that adjust for temperature and humidity based on real-time data help create a stable living environment for the hens, minimizing stress and promoting higher egg yield.
Additionally, advancements in breeding technologies have led to the development of hen strains that exhibit superior egg production and disease resistance. Genetic improvements mean that producers can select breeds that not only meet market demands for egg size and quality but also adapt better to environmental stresses.
Conclusion
The layer house represents an intersection of animal welfare, production efficiency, and technological prowess in the poultry farming sector. By prioritizing thoughtful design, rigorous management practices, and embracing technological advancements, poultry farmers can optimize their operations. A well-managed layer house not only supports the health and well-being of the hens but also enhances the overall productivity of egg production, contributing to a sustainable agricultural future. As the global demand for eggs continues to rise, the importance of efficient and humane poultry farming practices will only grow.
-
Automatic Feeding Line System - Anping Yize|Poultry Efficiency&Durability
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System-Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.|Durable PP Material&Easy Maintenance
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System-Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker|Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Hot Sale 24 & 18 Door Rabbit Cages - Premium Breeding Solutions
NewsJul.25,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker - Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.21,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker - Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.21,2025






