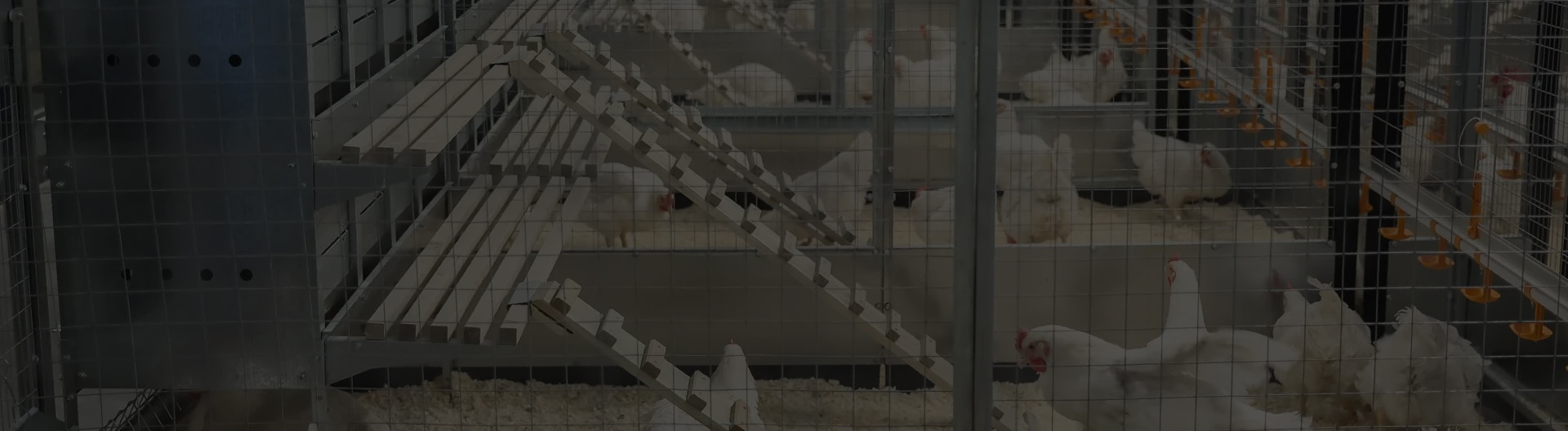
egg poultry farm cage
Dec . 12, 2024 18:18 Back to list
egg poultry farm cage
The Rise of Cage Farming in Egg Production A Comprehensive Overview
In recent years, the poultry farming industry has transformed dramatically, particularly in the egg production sector. One of the most significant changes has been the advent and implementation of cage farming systems. This method, while controversial, has become a dominant force in the industry due to its efficiency and productivity. This article delves into the practices, benefits, and criticisms associated with cage farming in egg production.
Cage farming, particularly the use of battery cages, involves housing hens in small, confined spaces to maximize productivity. These cages often contain several hens at a time and are designed to allow easy access for feeding, watering, and egg collection. This system enables farmers to manage large flocks with minimal labor, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of eggs to meet consumer demand.
The Rise of Cage Farming in Egg Production A Comprehensive Overview
However, the use of cages in poultry farming has raised ethical concerns regarding animal welfare. Critics argue that confining hens in small cages restricts their natural behaviors, leading to stress and discomfort. The inability for hens to engage in activities such as nesting, perching, or dust bathing has sparked widespread debate and calls for reform within the industry. Many animal rights organizations advocate for more humane treatments, leading to a growing movement against battery cages and promoting alternative farming systems.
egg poultry farm cage
In response to public outcry, some regions and countries have begun to implement regulations aimed at improving the welfare of hens. The European Union, for instance, has banned traditional battery cages, mandating the adoption of enriched cages that provide more space and features like nesting boxes and perches. This shift illustrates the growing awareness and sensitivity toward animal welfare in poultry farming.
Moreover, consumer preferences are also shifting. Many consumers are becoming more conscious of animal welfare and are willing to pay a premium for eggs produced in free-range or cage-free environments. As a result, some egg producers are transitioning from conventional cage systems to more humane alternatives to cater to this evolving market demand. This transition, however, presents challenges, including the need for larger farming spaces and changes in management practices, which can impact production costs.
Environmental sustainability is another critical aspect under scrutiny. Cage farming's intensive nature means a higher concentration of hens in a smaller area, potentially leading to waste management issues and environmental pollution. While these systems can be efficient, questions surrounding their long-term sustainability remain, especially as the global population continues to grow.
In conclusion, the rise of cage farming in egg production reflects the complexities of modern agriculture, balancing efficiency and productivity against ethical considerations and consumer preferences. While cage systems offer significant advantages in terms of production levels and management efficiency, they do not come without criticisms related to animal welfare and environmental sustainability. As the industry evolves, finding a consensus that addresses economic viability, animal welfare, and environmental responsibility will be crucial. The future of egg production may very well depend on how effectively poultry farmers can adapt to these changing demands while maintaining ethical practices that promote both the welfare of the hens and the health of the planet.
-
Automatic Feeding Line System-Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker|Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.29,2025
-
Hot Sale 24 & 18 Door Rabbit Cages - Premium Breeding Solutions
NewsJul.25,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker - Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.21,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System Pan Feeder Nipple Drinker - Anping County Yize Metal Products Co., Ltd.
NewsJul.21,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System - Anping Yize | Precision & Nipple
NewsJul.21,2025
-
Automatic Feeding Line System - Anping Yize | Precision & Nipple
NewsJul.21,2025






